Laboratory of Retinal Development and Disease
Children’s Hospital Los Angeles
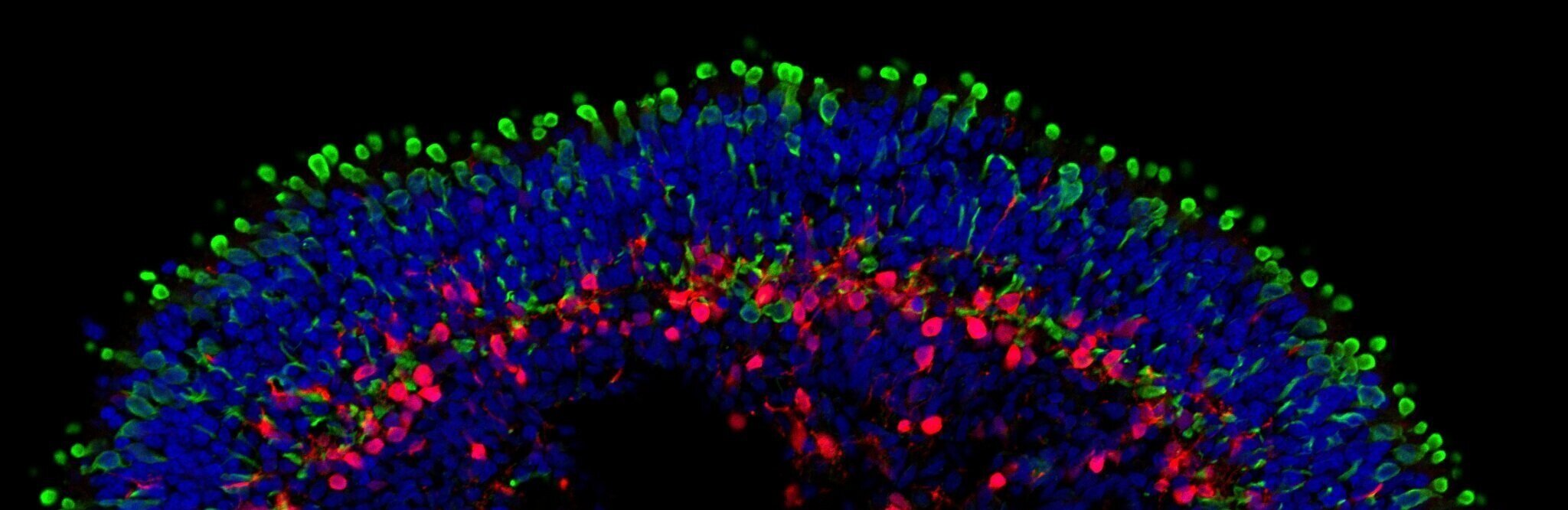
Synaptogenesis in the Human Retina
The development and maintenance of specific synaptic connections between retinal neurons is critical to its function. Within the last 10 years it has become possible to grow 3-dimensional, multi-layered retinal organoids derived from human stem cells. This advance permits the study of human retinal development and the establishment of synaptic connectivity. Our goal is to elucidate mechanisms underlying synapse formation and specificity in the first synapse of the human visual system. Access to CRISPR-engineered organoids allows us to understand this process in the disease state. Bharathan et al. (2021) Development.
Base Editing for Inherited Retinal Disease
The FDA approval of voretigene neparvovec-rzyl (Luxturna) for RPE65-mediated retinal dystrophies has ushered in an era of targeted molecular therapies for inherited retinal disease (IRD). In collaboration with David Cobrinik, Thomas Lee, and Jennifer Aparicio, we have initiated a personalized medicine program focused on the use of base editing for the treatment of IRDs. With access to patient-derived iPSCs, we can test variant-specific strategies for IRDs not amenable to gene augmentation such as autosomal dominant diseases.
Hippo Inhibition for Retinal Regeneration
Although single gene therapies represent an important therapeutic avenue, the sheer number of dystrophy genes (200+) makes broadly applicable, gene-agnostic small-molecule therapies an attractive alternative. Through a collaboration with Ksenia Gnedeva at USC, our group has unique access to a novel class of inhibitors targeting Hippo signaling – the major molecular pathway restricting Müller cell generation of photoreceptors in mammals. We are evaluating small-molecule Hippo inhibition using several in vitro and in vivo disease models. If successful, this approach would lead to endogenous regeneration of the retina with a simple clinic-based intravitreal injection of a small-molecule drug. Kastan and Gnedeva et al. (2021) Nature Comms.
Funding
The Saban Research Institute (CHLA) • Research to Prevent Blindness • Donald E. and Delia B. Baxter Foundation • Knights Templar Eye Foundation • National Eye Institute (K08 EY030924)


